
The autonomic nervous system has two subdivisions, the postganglionic neurons, which run to the effector organ (cardiac muscle, smooth muscle, or a gland).The first, the preganglionic neurons, arise in the CNS and run to a ganglion in the body.It also differs from the sensory-somatic system is using two groups of motor neurons to stimulate the effectors instead of one. The actions of the autonomic nervous system are largely involuntary (in contrast to those of the sensory-somatic system). The contraction of both smooth muscle and cardiac muscle is controlled by motor neurons of the autonomic system. It is responsible for monitoring conditions in the internal environment and bringing about appropriate changes in them. The autonomic nervous system consists of sensory neurons and motor neurons that run between the central nervous system (especially the hypothalamus and medulla oblongata) and various internal organs such as the: Link to a discussion of the mechanism by which the commands of the motor neurons of the sensory-somatic system are executed by skeletal muscles. Īll our conscious awareness of the external environment and all our motor activity to cope with it operate through the sensory-somatic division of the PNS. The Spinal NervesĪll of the spinal nerves are "mixed" that is, they contain both sensory and motor neurons. *Note: These do contain a few sensory neurons that bring back signals from the muscle spindles in the muscles they control. (Contain 38% of all the axons connecting to the brain.) The peripheral nervous system is subdivided into the motor neurons running from the CNS to the muscles and glands - called effectors - that take action.sensory neurons running from stimulus receptors that inform the CNS of the stimuli.Link to discussion of the central nervous system. peripheral nervous system ( PNS) and the.The autonomic nervous system controls internal organs and glands, while the somatic nervous system controls muscles and movement. The somatic nervous system has sensory and motor pathways, whereas the autonomic nervous system only has motor pathways.

The autonomic nervous system consists of two sub-components, whereas the somatic nervous system only has one. The sympathetic nervous system responds to external stimuli by preparing the body for fight or flight and the somatic nervous system responds to external stimuli (by carrying information from sensory receptors to the spinal cord and brain). The sympathetic nervous system (part of the autonomic nervous system) and the somatic nervous system respond to external stimuli. PERIPHERAL NERVOUS SYSTEM (somatic/autonomic & sympathetic/parasympathetic) The brain consists of multiple regions responsible for different functions, whereas the spinal cord has one main function.
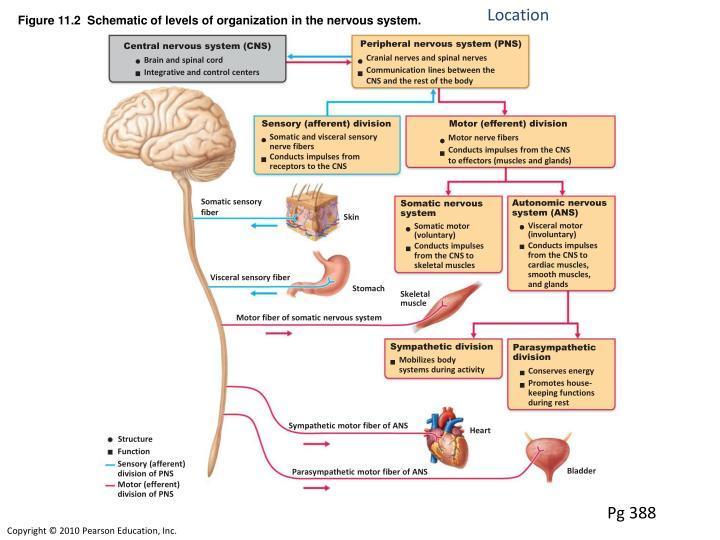
The brain provides conscious awareness and allows for higher-order thinking, while the spinal cord allows for simple reflex responses. the brain stem controls breathing and the spinal cord controls involuntary reflexes). The brain stem and spinal cord both control involuntary processes (e.g. Here are some key similarities and differences when comparing the CNS (Brain & spinal cord) and PNS (somatic/autonomic & sympathetic/parasympathetic).ĬENTRAL NERVOUS SYSTEM (brain & spinal cord)


 0 kommentar(er)
0 kommentar(er)
